Journal of Medical Science
Top Articles 
About Publishing

Cureus provides a smarter, affordable and hassle-free publishing experience. Learn more about the benefits of publishing with Cureus as well as how it all works!
Academic Channels

The subscription-based service that every academic department, medical school and medical society needs. Turn your organization into a publishing powerhouse with an academic channel.
Publishing Competitions

Position your organization as a thought leader and deliver relevant, peer-reviewed literature directly to potential customers with a Cureus publishing competition.
About Publishing

Cureus provides a smarter, affordable and hassle-free publishing experience. Learn more about the benefits of publishing with Cureus as well as how it all works!
Academic Channels

The subscription-based service that every academic department, medical school and medical society needs. Turn your organization into a publishing powerhouse with an academic channel.
Publishing Competitions

Position your organization as a thought leader and deliver relevant, peer-reviewed literature directly to potential customers with a Cureus publishing competition.
Discussions
 Vishal V. Bhende, MBBS
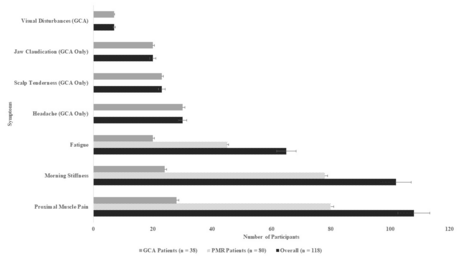
Vishal V. Bhende, MBBSLongevity is not reduced in patients with giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica unless severe aortitis is also present. Contrary to the previously held belief that giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica are self-limiting conditions, vasculitis persists in many, if not all, patients, although in most instances it does not causing life-threatening complications !!
 Patricia Rudolph
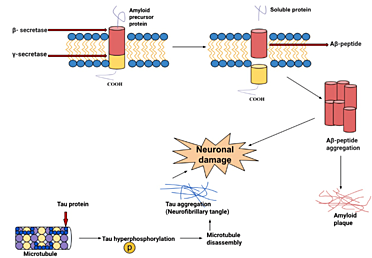
Patricia RudolphMy LO has been diagnosed with Alzheimer's officially for 5 years. Memory was lost, didn't remember his mother, or past life, acted like a 12 yr old. he was 75, He had some terrible night as he kept asking to go to the bathroom and get up at night. The doctor prescribed a sleeping pill (zolpidem), but it had a very bad side effect on him (delusions and hallucinations) and we decided not to give it any more and went for the Neuro X program that was introduced to us by his primary care doctor, he was on the Neuro X program for Alzheimer’s disease from Uine Health Centre for 6 months. The treatment relieved symptoms significantly, After the treatment he’s all of a sudden back active again, almost all his symptoms are gone, no signs of agitations, his sleeps pattern are back to normal. His memory loss has greatly improved and he tells stories about his past life, we got the Neuro X program from uinehealthcentre. com. I want to clarify that my comment is not a paid promotion or any form of advertisement. I am absolutely confident that this program offers a viable solution and hope someone find it helpful.





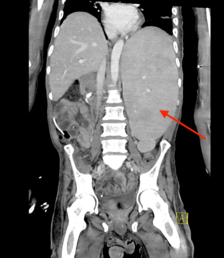
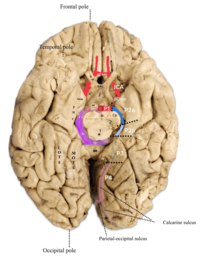
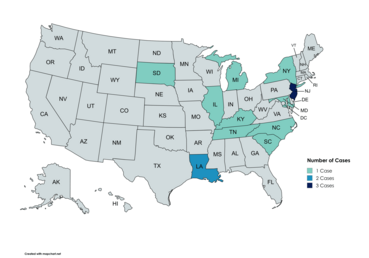
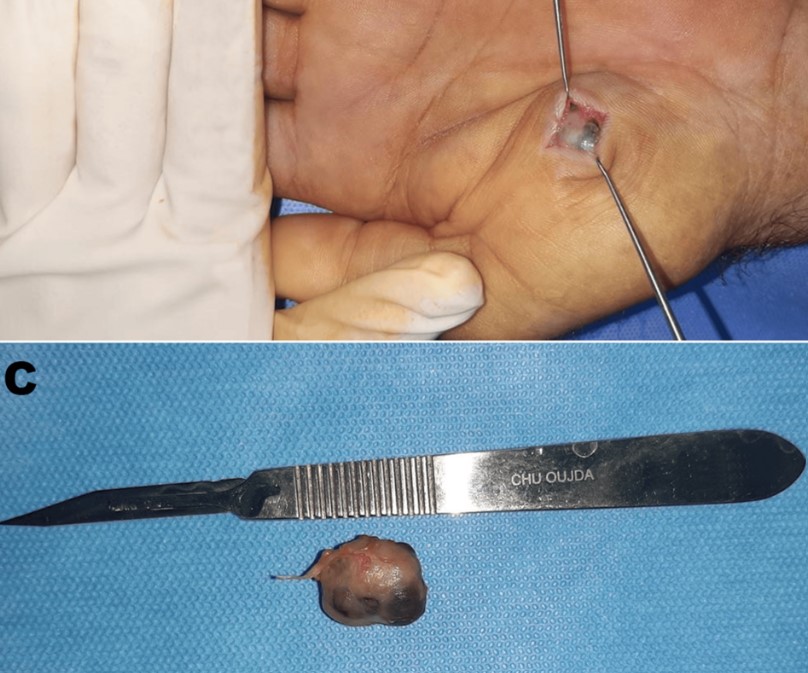









An insightful and well-researched article! Your findings provide valuable perspectives and contribute significantly to the field. Great work!