Abstract
Introduction: Many transgender individuals use medical intervention to facilitate transitions from their sex assigned at birth to the sex they identify with most. This intervention may be in the form of hormonal therapy, such as estrogen or testosterone, or surgery. Transgender patients may elect to have reaffirmation surgeries performed, such as augmentation, feminization surgery, vaginoplasty, or phalloplasty. This demographic commonly faces postoperative complications arising from these procedures.
Objective: The objective of this study is to first determine which surgeries performed in transgender patients are the most common, and second, to evaluate which postoperative complications most frequently occur. Additionally, this study aims to summarize the mechanisms behind why these complications arise in this specific patient population.
Methods: The CINAHL Complete (EBSCO) database was used to find articles pertaining to the topic of interest. Articles published from January 2000 to January 2023 were searched for using the terms “transgender” AND “surgery” AND “complications.” The data was selected for using the following criteria: The publications must have examined the transgender population. The articles must have studied surgical procedures in the desired patient population. Finally, the publications must have mentioned any kind of complications arising from the procedures. Surgeries were then grouped into two categories: gender affirmation operations (phalloplasty, vaginoplasty, colpectomy, hysterectomy) and aesthetic operations (chest wall reconstruction, facial hair transplantation, thyroid chondroplasty).
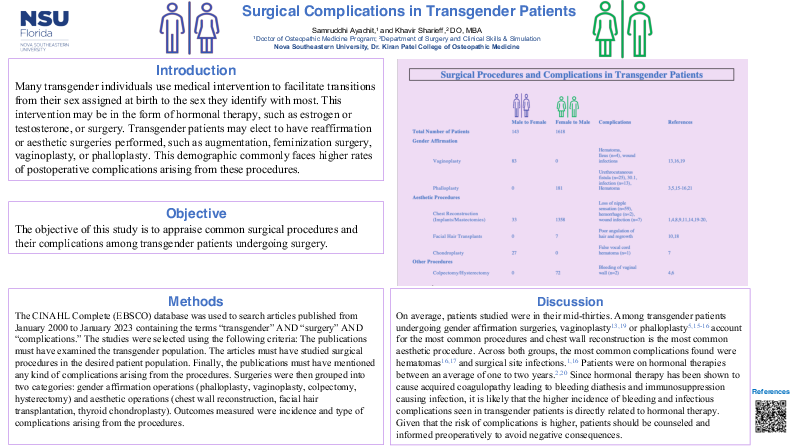
Results: A total of 46 articles were found using the aforementioned search terms. Of these 46 publications, 22 met the inclusion criteria. 1761 patients met these requirements. 14 of the articles meeting the requirements were classified as gender affirmation surgeries, and the remaining 8 focused on aesthetic operations. Amongst these 22 articles, the most common gender affirmation surgeries were vaginoplasties and phalloplasties. Within the aesthetic subcategory, the operation most frequently performed was chest wall reconstruction. Across both groups, the most common complications were found to be hematomas and infections. It is proposed that transgender patients are at risk for bleeding-associated post-operative complications because these patients are administered hormonal therapies, such as testosterone, to transition.
Conclusion: 22 articles containing a total of 1761 patients were examined. The information available shows that transgender patients undergoing gender affirmation surgeries, most commonly underwent either vaginoplasty or phalloplasty. On the contrary, patients needing aesthetic surgeries had chest reconstruction performed. When comparing both groups, hematoma formation was the most common complication reported. Transgender individuals have a higher risk of hematoma formation possibly due to hormonal therapies.